Blog
2020-02-16
This is the fifth post in a series of posts about my PhD thesis.
In the fifth and final chapter of my thesis, we look at how boundary conditions can be weakly imposed on the Helmholtz equation.
Analysis
As in chapter 4, we must adapt the analysis of chapter 3 to apply to Helmholtz problems. The boundary operators for the Helmholtz equation satisfy less strong
conditions than the operators for Laplace's equation (for Laplace's equation, the operators satisfy a condition called coercivity; for Helmholtz, the operators
satisfy a weaker condition called Gårding's inequality), making proving results about Helmholtz problem harder.
After some work, we are able to prove an a priori error bound (with \(a=\tfrac32\) for the spaces we use):
$$\left\|u-u_h\right\|\leqslant ch^{a}\left\|u\right\|$$
Numerical results
As in the previous chapters, we use Bempp to show that computations with this method match the theory.
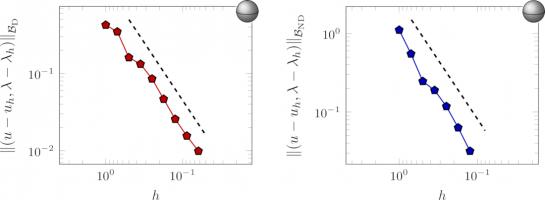
The error of our approximate solutions of a Dirichlet (left) and mixed Dirichlet–Neumann problems in the exterior of a sphere with
meshes with different values of \(h\). The dashed lines show order \(\tfrac32\) convergence.
Wave scattering
Boundary element methods are often used to solve Helmholtz wave scattering problems. These are problems in which a sound wave is travelling though a medium (eg the air),
then hits an object: you want to know what the sound wave that scatters off the object looks like.
If there are multiple objects that the wave is scattering off, the boundary element method formulation can get quite complicated. When using weak imposition,
the formulation is simpler: this one advantage of this method.
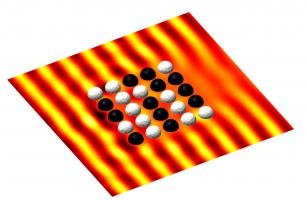
The following diagram shows a sound wave scattering off a mixure of sound-hard and sound-soft spheres.
Sound-hard objects reflect sound well, while sound-soft objects absorb it well.
If you are trying to design something with particular properties—for example, a barrier that absorbs sound—you may want to solve
lots of wave scattering problems on an object on some objects with various values taken for their reflective properties. This type of problem is often called an inverse problem.
For this type of problem, weakly imposing boundary conditions has advantages: the discretisation of the Calderón projector can be reused for each problem, and only the terms
due to the weakly imposed boundary conditions need to be recalculated. This is an advantages as the boundary condition terms are much less expensive (ie they use much less time and memory)
to calculate than the Calderón term that is reused.
This concludes chapter 5, the final chapter of my thesis.
Why not celebrate reaching the end by cracking open the following figure before reading the concluding blog post.
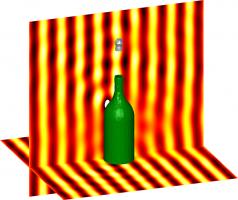
An acoustic wave scattering off a sound-hard champagne bottle and a sound-soft cork.
Previous post in series
This is the fifth post in a series of posts about my PhD thesis.
Next post in series
(Click on one of these icons to react to this blog post)
You might also enjoy...
Comments
Comments in green were written by me. Comments in blue were not written by me.
Add a Comment