Blog
Optimal Pac-Man
2015-03-25
This is an article which I wrote for the
first issue of
Chalkdust. I highly recommend reading the rest of the magazine (and trying
to solve the crossnumber I wrote for the issue).
In the classic arcade game Pac-Man, the player moves the title character through a maze. The aim of
the game is to eat all of the pac-dots that are spread throughout the maze while avoiding the ghosts
that prowl it.
While playing Pac-Man recently, my concentration drifted from the pac-dots and I began to think
about the best route I could take to complete the level.
Seven bridges of Königsberg
In the 1700s, Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler studied a related problem. The city of
Königsberg had seven bridges, which the residents would try to cross while walking around the
town. However, they were unable to find a route crossing every bridge without repeating one of them.
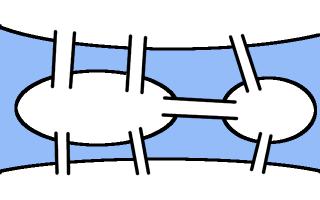
Diagram showing the bridges in Königsberg. If you have not
seen this puzzle before, you may like to try to find a route crossing them all exactly once before reading on.
In fact, the city dwellers could not find such a route because it is impossible to do so, as
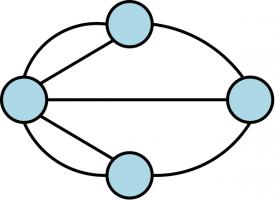
Euler proved in 1735. He first simplified the map of the city, by making the islands into vertices (or nodes)
and the bridges into edges.
This type of diagram has (slightly confusingly) become known as a graph, the study of which is
called graph theory. Euler represented Königsberg in this way as he realised that the shape of the
islands is irrelevant to the problem: representing the problem as a graph gets rid of this useless information
while keeping the important details of how the islands are connected.
Euler next noticed that if a route crossing all the bridges exactly once was possible then whenever
the walker took a bridge onto an island, they must take another bridge off the island. In this way,
the ends of the bridges at each island can be paired off. The only bridge ends that do not need a
pair are those at the start and end of the circuit.
This means that all of the vertices of the graph except two (the first and last in the route) must have an even number of edges connected to them; otherwise there is no route around the graph
travelling along each edge exactly once. In Königsberg, each island is connected to an odd number of bridges. Therefore the route that
the residents were looking for did not exist (a route now exists due to two of the bridges being destroyed during World War II).
This same idea can be applied to Pac-Man. By ignoring the parts of the maze without pac-dots the pac-graph
can be created, with the paths and the junctions forming the edges and vertices respectively. Once this
is done there will be twenty-four vertices, twenty of which will be connected to an odd number of edges, and so it is impossible to eat
all of the pac-dots without repeating some edges or travelling along parts of the maze with no pac-dots.
This is a start, but it does not give us the shortest route we can take to eat all of the pac-dots: in
order to do this, we are going to have to look at the odd vertices in more detail.
The Chinese postman problem
The task of finding the shortest route covering all the edges of a graph has become known as the
Chinese postman problem as it is faced by postmen—they need to walk along each street to post
letters and want to minimise the time spent walking along roads twice—and it was first studied by
Chinese mathematician Kwan Mei-Ko.
As the seven bridges of Königsberg problem demonstrated, when trying to find a route, Pac-Man
will get stuck at the odd vertices. To prevent this from happening, all the vertices can be made into even
vertices by adding edges to the graph. Adding an edge to the graph corresponds to choosing an edge, or sequence
of edges, for Pac-Man to repeat or including a part of the maze without pac-dots. In order to complete the level
with the shortest distance travelled, Pac-Man wants to add the shortest total length of edges to the graph.
Therefore, in order to find the best route, Pac-Man must look at different ways to pair off the odd vertices and choose
the pairing which will add the least total distance to the graph.
The Chinese postman problem and the Pac-Man problem are slightly different: it is usually assumed
that the postman wants to finish where he started so he can return home. Pac-Man however can finish
the level wherever he likes but his starting point is fixed. Pac-Man may therefore leave one odd
node unpaired but must add an edge to make the starting node odd.
One way to find the required route is to look at all possible ways to pair up the odd vertices. With a low
number of odd vertices this method works fine, but as the number of odd vertices increases, the
method quickly becomes slower.
With four odd vertices, there are three possible pairings. For the Pac-Man problem there will be
over 13 billion (\(1.37\times 10^{10}\)) pairings to check. These pairings can be checked by a
laptop running overnight, but for not too many more vertices this method quickly becomes unfeasible.
With 46 odd nodes there will be more than one pairing per atom in the human body (\(2.53\times 10^{28}\)).
By 110 odd vertices there will be more pairings (\(3.47\times 10^{88}\)) than there are estimated to be atoms in the
universe. Even the greatest supercomputer will be unable to work its way through
all these combinations.
Better algorithms are known for this problem that reduce the amount of work on larger graphs. The number of
pairings to check in the method above increases like the factorial of the number of vertices. Algorithms are
known for which the amount of work to be done increases like a polynomial in the number of vertices. These algorithms
will become unfeasible at a much slower rate but will still be unable to deal with very large graphs.
Solution of the Pac-Man problem
For the Pac-Man problem, the shortest pairing of the odd vertices requires the edges marked in red to be
repeated. Any route which repeats these edges will be optimal. For example, the route in green will be
optimal.
One important element of the Pac-Man gameplay that I have neglected are the ghosts (Blinky, Pinky,
Inky and Clyde), which Pac-Man must avoid. There is a high chance that the ghosts will at some point
block the route shown above and ruin Pac-Man's optimality. However, any route repeating the red edges
will be optimal: at many junctions Pac-Man will have a choice of edges he could continue along. It may
be possible for a quick thinking player to utilise this freedom to avoid the ghosts and complete an optimal
game.
Additionally, the skilled player may choose when to take the edges that include the power pellets,
which allow Pac-Man to reverse the roles and eat the ghosts. Again cleverly timing these may allow
the player to complete an optimal route.
Unfortunately, as soon as the optimal route is completed, Pac-Man moves to the next level and the
player has to do it all over again ad infinitum.
A video
Since writing this piece, I have been playing Pac-Man using
MAME (Multiple Arcade Machine Emulator). Here is one game I played along
with the optimal edges to repeat for reference:

(Click on one of these icons to react to this blog post)
You might also enjoy...
Comments
Comments in green were written by me. Comments in blue were not written by me.
This vid was billed as an "optimal" run but around 40 seconds in you eat one "pill" that you don't need to eat. Why don't you just speedrun the first level? This must have been done before. Can you beat the world record?
William
Add a Comment





There seems to be no world record for just one Pac-Man level (and I don't have time to get good enough to speed run all 255 levels before it crashes!)