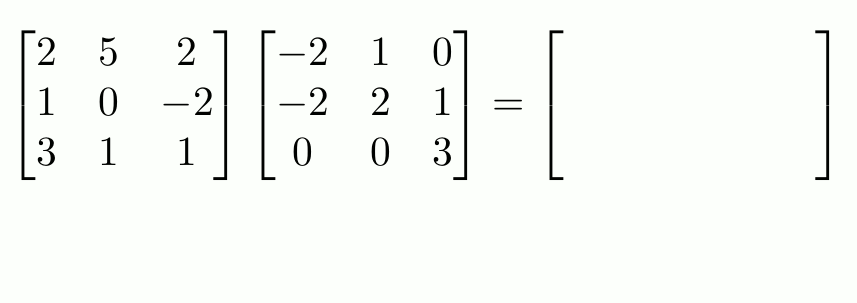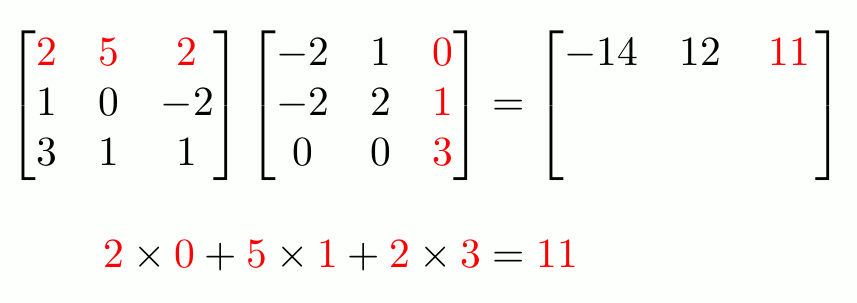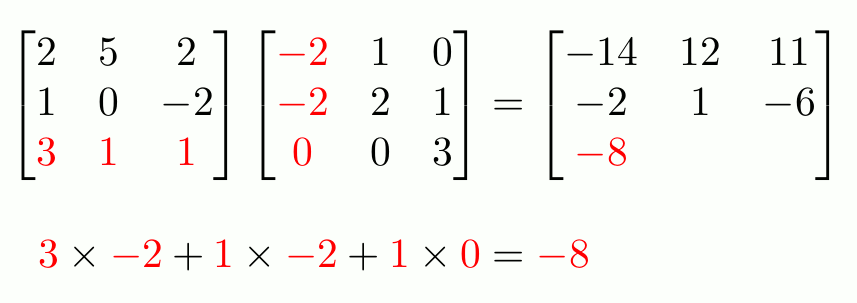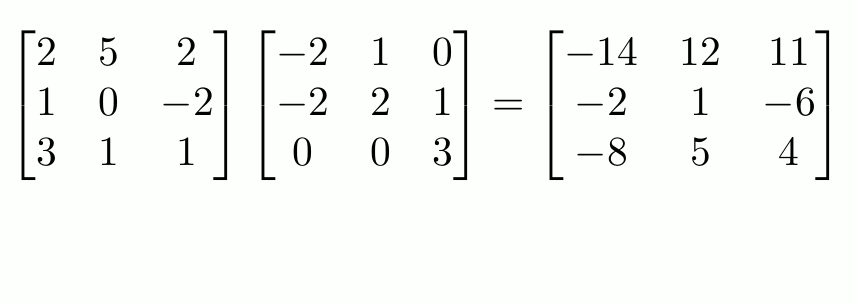Blog
2020-01-23
This is the first post in a series of posts about matrix methods.
When you first learn about matrices, you learn that in order to multiply two matrices, you use this strange-looking method involving the rows of the left matrix and the columns of this right.
It doesn't immediately seem clear why this should be the way to multiply matrices. In this blog post, we look at why this is the definition of matrix multiplication.
Simultaneous equations
Matrices can be thought of as representing a system of simultaneous equations. For example, solving the matrix problem
$$
\begin{bmatrix}2&5&2\\1&0&-2\\3&1&1\end{bmatrix}
\begin{pmatrix}x\\y\\z\end{pmatrix}
=
\begin{pmatrix}14\\-16\\-4\end{pmatrix}
$$
is equivalent to solving the following simultaneous equations.
\begin{align*}
2x+5y+2z&=14\\
1x+0y-2z&=-16\\
3x+1y+1z&=-4
\end{align*}
Two matrices
Now, let \(\mathbf{A}\) and \(\mathbf{C}\) be two 3×3 matrices, let \(\mathbf{b}\) by a vector with three elements, and let \(\mathbf{x}=(x,y,z)\).
We consider the equation
$$\mathbf{A}\mathbf{C}\mathbf{x}=\mathbf{b}.$$
In order to understand what this equation means, we let \(\mathbf{y}=\mathbf{C}\mathbf{x}\) and think about solving the two simuntaneous matrix equations,
\begin{align*}
\mathbf{A}\mathbf{y}&=\mathbf{b}\\
\mathbf{C}\mathbf{x}&=\mathbf{y}.
\end{align*}
We can write the entries of \(\mathbf{A}\), \(\mathbf{C}\), \(\mathbf{x}\), \(\mathbf{y}\) and \(\mathbf{b}\) as
\begin{align*}
\mathbf{A}&=\begin{bmatrix}
a_{11}&a_{12}&a_{13}\\
a_{21}&a_{22}&a_{23}\\
a_{31}&a_{32}&a_{23}
\end{bmatrix}
&
\mathbf{C}&=\begin{bmatrix}
c_{11}&c_{12}&c_{13}\\
c_{21}&c_{22}&c_{23}\\
c_{31}&c_{32}&c_{23}
\end{bmatrix}
\end{align*}
\begin{align*}
\mathbf{x}&=\begin{pmatrix}x_1\\x_2\\x_3\end{pmatrix}
&
\mathbf{y}&=\begin{pmatrix}y_1\\y_2\\y_3\end{pmatrix}
&
\mathbf{b}&=\begin{pmatrix}b_1\\b_2\\b_3\end{pmatrix}
\end{align*}
We can then write out the simultaneous equations that \(\mathbf{A}\mathbf{y}=\mathbf{b}\) and \(\mathbf{C}\mathbf{x}=\mathbf{y}\) represent:
\begin{align}
a_{11}y_1+a_{12}y_2+a_{13}y_3&=b_1&
c_{11}x_1+c_{12}x_2+c_{13}x_3&=y_1\\
a_{21}y_1+a_{22}y_2+a_{23}y_3&=b_2&
c_{21}x_1+c_{22}x_2+c_{23}x_3&=y_2\\
a_{31}y_1+a_{32}y_2+a_{33}y_3&=b_3&
c_{31}x_1+c_{32}x_2+c_{33}x_3&=y_3\\
\end{align}
Substituting the equations on the right into those on the left gives:
\begin{align}
a_{11}(c_{11}x_1+c_{12}x_2+c_{13}x_3)+a_{12}(c_{21}x_1+c_{22}x_2+c_{23}x_3)+a_{13}(c_{31}x_1+c_{32}x_2+c_{33}x_3)&=b_1\\
a_{21}(c_{11}x_1+c_{12}x_2+c_{13}x_3)+a_{22}(c_{21}x_1+c_{22}x_2+c_{23}x_3)+a_{23}(c_{31}x_1+c_{32}x_2+c_{33}x_3)&=b_2\\
a_{31}(c_{11}x_1+c_{12}x_2+c_{13}x_3)+a_{32}(c_{21}x_1+c_{22}x_2+c_{23}x_3)+a_{33}(c_{31}x_1+c_{32}x_2+c_{33}x_3)&=b_3\\
\end{align}
Gathering the terms containing \(x_1\), \(x_2\) and \(x_3\) leads to:
\begin{align}
(a_{11}c_{11}+a_{12}c_{21}+a_{13}c_{31})x_1
+(a_{11}c_{12}+a_{12}c_{22}+a_{13}c_{32})x_2
+(a_{11}c_{13}+a_{12}c_{23}+a_{13}c_{33})x_3&=b_1\\
(a_{21}c_{11}+a_{22}c_{21}+a_{23}c_{31})x_1
+(a_{21}c_{12}+a_{22}c_{22}+a_{23}c_{32})x_2
+(a_{21}c_{13}+a_{22}c_{23}+a_{23}c_{33})x_3&=b_2\\
(a_{31}c_{11}+a_{32}c_{21}+a_{33}c_{31})x_1
+(a_{31}c_{12}+a_{32}c_{22}+a_{33}c_{32})x_2
+(a_{31}c_{13}+a_{32}c_{23}+a_{33}c_{33})x_3&=b_3
\end{align}
We can write this as a matrix:
$$
\begin{bmatrix}
a_{11}c_{11}+a_{12}c_{21}+a_{13}c_{31}&
a_{11}c_{12}+a_{12}c_{22}+a_{13}c_{32}&
a_{11}c_{13}+a_{12}c_{23}+a_{13}c_{33}\\
a_{21}c_{11}+a_{22}c_{21}+a_{23}c_{31}&
a_{21}c_{12}+a_{22}c_{22}+a_{23}c_{32}&
a_{21}c_{13}+a_{22}c_{23}+a_{23}c_{33}\\
a_{31}c_{11}+a_{32}c_{21}+a_{33}c_{31}&
a_{31}c_{12}+a_{32}c_{22}+a_{33}c_{32}&
a_{31}c_{13}+a_{32}c_{23}+a_{33}c_{33}
\end{bmatrix}
\mathbf{x}=\mathbf{b}
$$
This equation is equivalent to \(\mathbf{A}\mathbf{C}\mathbf{x}=\mathbf{b}\), so the matrix above is equal to \(\mathbf{A}\mathbf{C}\). But this matrix is what you get if follow the
row-and-column matrix multiplication method, and so we can see why this definition makes sense.
This is the first post in a series of posts about matrix methods.
Next post in series
(Click on one of these icons to react to this blog post)
You might also enjoy...
Comments
Comments in green were written by me. Comments in blue were not written by me.
Add a Comment