Blog
2025-01-01
The puzzle on day 23 of this year's Advent calendar
is an interesting puzzle. After some hasty editing once it was pointed out to me that the original wording
was nonsense, the puzzle was this:
23 December
In a grid of squares, each square is friendly with itself and friendly with every square that is horizontally, vertically, or diagonally adjacent to it (and is not friendly with any other squares).
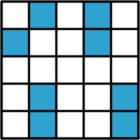
In a 5×5 grid, it is possible to colour 8 squares so that every square is friendly with at least two coloured squares:
It it not possible to do this by colouring fewer than 8 squares.
What is the fewest number of squares that need to be coloured in a
23×23 grid so that every square is friendly with at least two coloured squares?
As the squares that a square is friendly with are the same as those that would be attacked by a chess king on the square, the puzzle could be
re-expressed as: What is the fewest number of kings that need to be placed on a 23×23 chess board so that every square is attacked or occupied by at least two kings
(with no more than one king placed on each square)?
I came up with this puzzle while playing around with square grids in early November last year. I started by working out how many squares
need to be coloured for some smaller grids:
| Size of grid | Example grid | Minimum number of squares | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2×2 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3×3 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4×4 | 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5×5 | 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6×6 | 10 |
This sequence was not on the OEIS, so I set about trying to work out the general formula for a term in this sequence.
Let \(a(n)\) be the minimum number of squared coloured for an \(n\) by \(n\) grid.
To work out the formula for \(a(n)\), we'll split the problem into 3 cases:
when \(n\) is a multiple of 3,
when \(n\) is 1 less than a multiple of 3,
when \(n\) is 2 less than a multiple of 3.
\(n=3k-1\)
When \(n\) is 1 less than a multiple of 3, it can be written as \(3k-1\) for some integer \(k\).
An upper bound
We can get an upper bound for the number of squares by finding a pattern of coloured squares that works, as the minimum number of squares will
then be at most this. For a 2×2 grid, we can colour 2 squares like this:
For a 5×5 grid, we can colour 8 squares like this:
For an 8×8 grid, we can colour 18 squares like this:
We can continue this pattern: in general for a \((3k-1)\)×\((3k-1)\) grid, we colour in pairs of squares with a gap of one between them in every third row.
This would involve colouring \(k\) rows of \(2k\) squares, so a total of \(2k^2\) squares.
Therefore \(a(3k-1)\leqslant2k^2\).
A lower bound
To obtain a lower bound, consider these squares in 5×5 grid:
or these squares in 8×8 grid:
The squares that neighbour these highlighted squares do not overlap, so two different squares must be coloured for each of these. This means that at least
2×4 (for a 5×5 grid) and 2×9 (for a 8×8 grid) squares must be coloured.
Continuing the pattern of highlighting the squares in every third row and every third column, we see that for a \((2k-1)\)×\((2k-1)\) grid, we must colour
at least \(2k^2\) squares, and so \(a(3k-1)\geqslant2k^2\).
The general term
Combining the lower and upper bounds, we can see that \(2k^2\leqslant a(3k-1)\leqslant2k^2\), and so \(a(3k-1)=2k^2\). As 23 is one less than a multiple of 3,
this first case is enough to solve the puzzle in the Advent calendar.
\(n=3k-2\)
When \(n\) is 2 less than a multiple of 3, it can be written as \(3k-2\) for some integer \(k\). We can obtain upper and lower bounds in a very similar way.
An upper bound
To get an upper bound, consider this pattern of coloured squares:
For a \((3k-2)\)×\((3k-2)\) grid, this pattern involves colouring \(k\) rows of \(2k\) squares, and so \(a(3k-2)\leqslant2k^2\).
A lower bound
To get a lower bound, consider this pattern of highlighted squares:
In exactly the same was as for \(n=3k-1\), we can see from this pattern that \(a(3k-2)\geqslant2k^2\).
The general term
Once again, our upper and lower bounds are equal, and so \(a(3k-2)=2k^2\).
\(n=3k\)
Here's where this question gets trickier/more interesting. If \(n\) is a multiple of 3, then it can be written at \(3k\) for some integer \(k\).
An upper bound
We can obtain an upper bound from this pattern:
For a \(3k\)×\(3k\) grid, this pattern involved colouring \(k\) rows of \(2k+1\) squares, and so \(a(3k)\leqslant2k^2+k\).
A lower bound
As in the previous sections, we can get an lower bound using this pattern:
For a \(3k\)×\(3k\) grid, the lower bound requires at least \(2k^2\) squares to be coloured.
We can increase this lower bound by 1 by looking at the
bottom right corner: the previous lower bound can colour at most one square adjacent to this, so there must be at least one more square next to that corner coloured.
So we have arrived at the lower bound \(a(3k)\geqslant2k^2+1\).
Bounds
In this case, the lower and upper bounds are not the same, so we are left with \(2k^2+1\leqslant a(3k)\leqslant 2k^2+k\). I've written
a Python script to compute terms of this sequence and have used it to find that:
- \(a(3)=3\)
- \(a(6)=10\)
- \(a(9)=21\)
- \(a(12)=36\)
For \(n=12\) and larger than this, the script takes a very long time, so I haven't checked any more terms.
The sequence and a conjecture
Overall, we've shown that:
$$
a(n) = \begin{cases}
2k^2&\text{if }n=3k-1\\
2k^2&\text{if }n=3k-2\\
\text{between }2k^2+1\text{ and }2k^2+k&\text{if }n=3k
\end{cases}
$$
This can be written slightly more succinctly as (where \(\lfloor x\rfloor\) means \(x\) rounded down to an integer):
$$
a(n) = \begin{cases}
\text{between }2\left(\frac{n}3\right)^2+1\text{ and }2\left(\frac{n}3\right)^2+\frac{n}3&\text{if }n\text{ is a multiple of 3}\\
2\left\lfloor\frac{n+2}3\right\rfloor^2&\text{if }n\text{ is not a multiple of 3}
\end{cases}
$$
I've submitted the sequence I have so far to the OEIS: A379726.
Based on the terms computed above, I conjecture that \(a(3k)=2k^2 + k\). If you have any ideas how I could increase my lower bound, or for any other way I could prove this, let me know!
Edit: OEIS sequence is published!
(Click on one of these icons to react to this blog post)
You might also enjoy...
Comments
Comments in green were written by me. Comments in blue were not written by me.
Here is my solution:
Project
Pre-built
Probably not super useful as I didn't attempt to prove my results, but I did come up with a general formula for odd-sized squares (with floor and ceiling functions), and perhaps the way I decoupled the two dimensions could be a useful approach for you.
Project
Pre-built
Probably not super useful as I didn't attempt to prove my results, but I did come up with a general formula for odd-sized squares (with floor and ceiling functions), and perhaps the way I decoupled the two dimensions could be a useful approach for you.
Dan Whitman
The conjecture is correct. Super-brief sketch proof: divide the grid into 3x3 boxes, aggregate those into horizontal and vertical strips of width 1 box = 3 squares; say a strip is "cheap" if it contains only 2k shaded squares (hence, exactly two per box). Working box by box from one end of a cheap strip to the other in both directions we see that the shaded squares must be in the middle transverse row/column of each box in such a strip. Hence there can't be both a cheap horizontal strip and a cheap vertical strip, because the box where they meet is overconstrained. So either all h-strips are not-cheap or all v-strips are not-cheap, and either of those gives you at least 2k2+k shaded squares.
(This, along with everything M.S. wrote, generalizes straightforwardly to arbitrary rectangular grids.)
(This, along with everything M.S. wrote, generalizes straightforwardly to arbitrary rectangular grids.)
g
Add a Comment




2x2: 6
3x3: 2
4x4: 1296
5x5: 371
6x6: 8
Haven't been able to go any farther with my current script, but for what it's worth, here it is on GitHub.