Blog
2015-10-21
This post also appeared on the Chalkdust Magazine blog.
If you're like me, then you will be disappointed that all of the home nations have been knocked out of the Rugby World Cup. If you're really like me, doing some maths related to rugby will cheer you up...
The scoring system in rugby awards points in packets of 3, 5 and 7. This leads a number of interesting questions that you can find in my guest puzzle on Alex Bellos's Guardian blog. In this blog post, we will focus on another area of rugby: conversion kicking.
Conversion kicks
When a try is scored by putting the ball down behind the line, the scoring team gets to take a conversion kick. This kick must be taken in line with where the try was scored but it is up to the kicker how far away the kick should be taken. But how far back should the ball be taken to make the kick easiest?
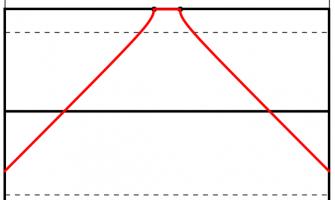
Too close (red) and too far away (blue) will give small angles to aim at. Somewhere in the middle is needed (green).
One way to answer this question is to look to maximise the angle between the posts which the kicker will have to aim at: if the kick is taken too close to or too far from the goal line there will be a very thin angle to aim at. Somewhere between these extremes there will be a maximum angle to aim at.
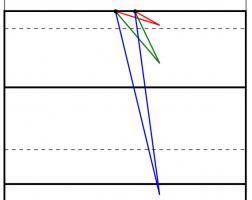
When looking to maximise this angle, we can use one of the 'circle theorems' which have tormented many generations of GCSE maths students: 'angles subtended by the same arc at the circumference are equal'. This means that if a circle is drawn going through both posts, then the angle made at any point on this circle will be the same.
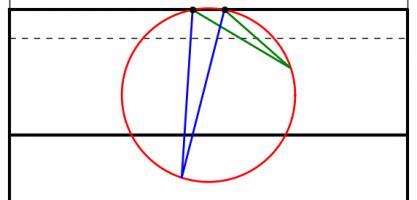
The angles made by the red and blue lines are equal because 'angles subtended by the same arc at the circumference are equal'.
A larger circle drawn through the posts will give a smaller angle. If a vertical line is drawn which just touches the right of the circle, then the point at which it touches the circle will be the best place on this line to take a kick. This is because any other point on the line will be on a larger circle and so make a smaller angle.
Using this method for circles of different sizes leads to the following diagram, which shows where the kick should be taken for every position a try could be scored:
This, however, is not the best place to take the kick.
Taking account of height
When a try is scored near the posts, the above method recommends a position from where the ball must be kicked at an impossibly steep angle to go over. To deal with this problem, we are going to have to look at the situation from the side.
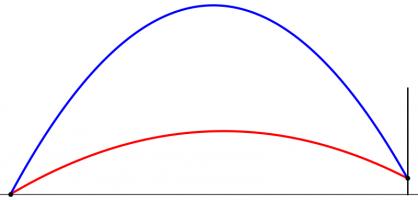
When kicked, the ball will travel along a parabola (ignoring air resistance and wind as their effects will be small[citation needed]). Given a distance from the posts, there will be two angles which the ball can be kicked at and just make it over the bar. Kicking at any angle between these two will lead to a successful conversion. Again, we have an angle which we would like to maximise.
However, the position where this angle is maximised is very unlikely to also maximise the angle we looked at earlier. To find the best place to kick from, we need to find a compromise point where both angles are quite big.
To do this, imagine that the kicker is standing inside a large sphere. For each point on the sphere, kicking the ball at the point will either lead to it going over or missing. We can draw a shape on the sphere so that aiming inside the shape will lead to scoring. Our sensible kicker will aim at the centre of this shape.
But our kicker will not be able to aim perfectly: there will be some random variation. We can predict that this variation will follow a Kent distribution, which is like a normal distribution but on the surface of a sphere. We can use this distribution to calculate the probability that our kicker will score. We would like to maximise this probability.
The Kent distribution can be adjusted to reflect the accuracy of the kicker. Below are the optimal kicking positions for an inaccurate, an average and a very accurate kicker.
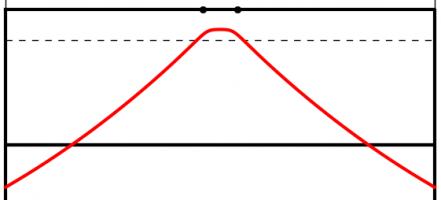
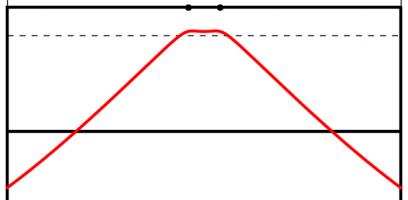
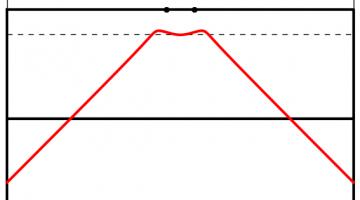
The best place to take a kick for a bad kicker (top), an average kicker (middle) and a good kicker (bottom). All the kickers kick the ball at 30m/s.
As you might expect, the less accurate kicker should stand slightly further forwards to make it easier to aim. Perhaps surprisingly, the good kicker should stand further back when between the posts than when in line with the posts.
The model used to create these results could be further refined. Random variation in the speed of the kick could be introduced. Or the kick could be made to have more variation horizontally than vertically: there are parameters in the Kent distribution which allow this to be easily adjusted. In fact, data from players could be used to determine the best position for each player to kick from.
In addition to analysing conversions, this method could be used to determine the probability of scoring 3 points from any point on the pitch. This could be used in conjunction with the probability of scoring a try from a line-out to decide whether kicking a penalty for the posts or into touch is likely to lead to the most points.
Although estimating the probability of scoring from a line-out is a difficult task. Perhaps this will give you something to think about during the remaining matches of the tournament.
(Click on one of these icons to react to this blog post)
You might also enjoy...
Comments
Comments in green were written by me. Comments in blue were not written by me.
Add a Comment