Blog
2019-04-09
In the latest issue of Chalkdust,
I wrote an article
with Edmund Harriss about the Harriss spiral that appears on the cover of the magazine.
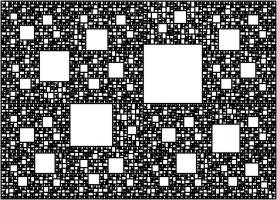
To draw a Harriss spiral, start with a rectangle whose side lengths are in the plastic ratio; that is the ratio \(1:\rho\)
where \(\rho\) is the real solution of the equation \(x^3=x+1\), approximately 1.3247179.
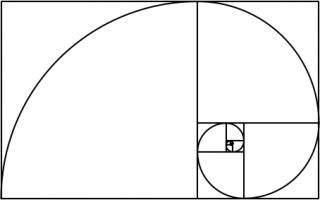
This rectangle can be split into a square and two rectangles similar to the original rectangle. These smaller rectangles can then be split up in the same manner.
Drawing two curves in each square gives the Harriss spiral.
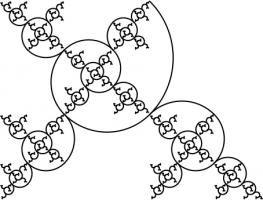
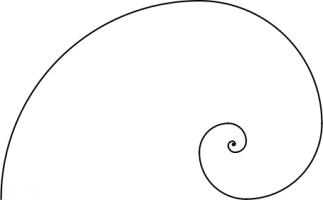
This spiral was inspired by the golden spiral, which is drawn in a rectangle whose side lengths are in the golden ratio of \(1:\phi\),
where \(\phi\) is the positive solution of the equation \(x^2=x+1\) (approximately 1.6180339). This rectangle can be split into a square and one
similar rectangle. Drawing one arc in each square gives a golden spiral.
The golden and Harriss spirals are both drawn in rectangles that can be split into a square and one or two similar rectangles.
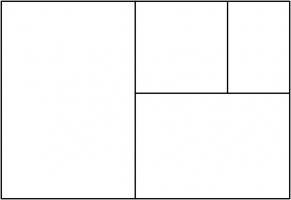
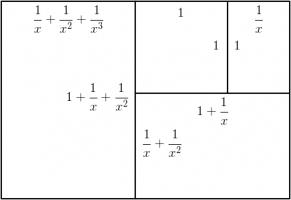
Continuing the pattern of these arrangements suggests the following rectangle, split into a square and three similar rectangles:
Let the side of the square be 1 unit, and let each rectangle have sides in the ratio \(1:x\). We can then calculate that the lengths of
the sides of each rectangle are as shown in the following diagram.
The side lengths of the large rectangle are \(\frac{1}{x^3}+\frac{1}{x^2}+\frac2x+1\) and \(\frac1{x^2}+\frac1x+1\). We want these to also
be in the ratio \(1:x\). Therefore the following equation must hold:
$$\frac{1}{x^3}+\frac{1}{x^2}+\frac2x+1=x\left(\frac1{x^2}+\frac1x+1\right)$$
Rearranging this gives:
$$x^4-x^2-x-1=0$$
$$(x+1)(x^3-x^2-1)=0$$
This has one positive real solution:
$$x=\frac13\left(
1
+\sqrt[3]{\tfrac12(29-3\sqrt{93})}
+\sqrt[3]{\tfrac12(29+3\sqrt{93})}
\right).$$
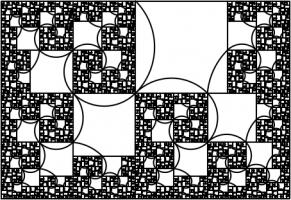
This is equal to 1.4655712... Drawing three arcs in each square allows us to make a spiral from a rectangle with sides in this ratio:
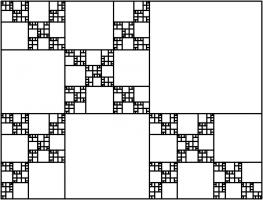
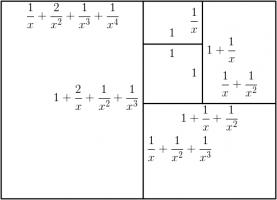
Adding a fourth rectangle leads to the following rectangle.
The side lengths of the largest rectangle are \(1+\frac2x+\frac3{x^2}+\frac1{x^3}+\frac1{x^4}\) and \(1+\frac2x+\frac1{x^2}+\frac1{x^3}\).
Looking for the largest rectangle to also be in the ratio \(1:x\) leads to the equation:
$$1+\frac2x+\frac3{x^2}+\frac1{x^3}+\frac1{x^4} = x\left(1+\frac2x+\frac1{x^2}+\frac1{x^3}\right)$$
$$x^5+x^4-x^3-2x^2-x-1 = 0$$
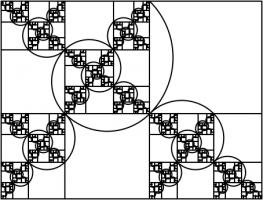
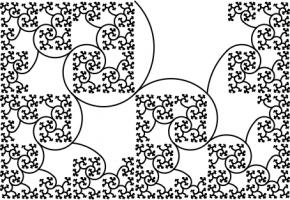
This has one real solution, 1.3910491... Although for this rectangle, it's not obvious which arcs to draw to make a
spiral (or maybe not possible to do it at all). But at least you get a pretty fractal:
We could, of course, continue the pattern by repeatedly adding more rectangles. If we do this, we get the following polynomials
and solutions:
| Number of rectangles | Polynomial | Solution |
| 1 | \(x^2 - x - 1=0\) | 1.618033988749895 |
| 2 | \(x^3 - x - 1=0\) | 1.324717957244746 |
| 3 | \(x^4 - x^2 - x - 1=0\) | 1.465571231876768 |
| 4 | \(x^5 + x^4 - x^3 - 2x^2 - x - 1=0\) | 1.391049107172349 |
| 5 | \(x^6 + x^5 - 2x^3 - 3x^2 - x - 1=0\) | 1.426608021669601 |
| 6 | \(x^7 + 2x^6 - 2x^4 - 3x^3 - 4x^2 - x - 1=0\) | 1.4082770325090774 |
| 7 | \(x^8 + 2x^7 + 2x^6 - 2x^5 - 5x^4 - 4x^3 - 5x^2 - x - 1=0\) | 1.4172584399350432 |
| 8 | \(x^9 + 3x^8 + 2x^7 - 5x^5 - 9x^4 - 5x^3 - 6x^2 - x - 1=0\) | 1.412713760332943 |
| 9 | \(x^{10} + 3x^9 + 5x^8 - 5x^6 - 9x^5 - 14x^4 - 6x^3 - 7x^2 - x - 1=0\) | 1.414969877544769 |
The numbers in this table appear to be heading towards around 1.414, or \(\sqrt2\).
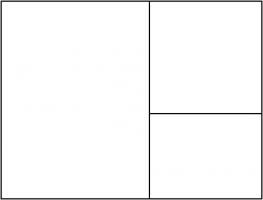
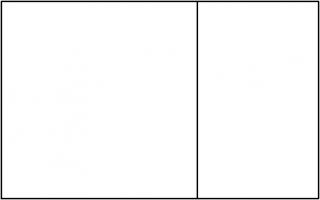
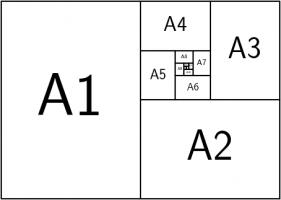
This shouldn't come as too much of a surprise because \(1:\sqrt2\) is the ratio of the sides of A\(n\) paper (for \(n=0,1,2,...\)).
A0 paper can be split up like this:
This is a way of splitting up a \(1:\sqrt{2}\) rectangle into an infinite number of similar rectangles, arranged following the pattern,
so it makes sense that the ratios converge to this.
Other patterns
In this post, we've only looked at splitting up rectangles into squares and similar rectangles following a particular pattern. Thinking about
other arrangements leads to the following question:
Given two real numbers \(a\) and \(b\), when is it possible to split an \(a:b\) rectangle into squares and \(a:b\) rectangles?
If I get anywhere with this question, I'll post it here. Feel free to post your ideas in the comments below.
(Click on one of these icons to react to this blog post)
You might also enjoy...
Comments
Comments in green were written by me. Comments in blue were not written by me.
2019-05-02
@g0mrb: CORRECTION: There seems to be no way to correct the glaring error in that comment. A senior moment enabled me to reverse the nomenclature for paper sizes. Please read the suffixes as (n+1), (n+2), etc.(anonymous)
I shall remain happy in the knowledge that you have shown graphically how an A(n) sheet, which is 2 x A(n-1) rectangles, is also equal to the infinite series : A(n-1) + A(n-2) + A(n-3) + A(n-4) + ... Thank-you, and best wishes for your search for the answer to your question.
g0mrb
Add a Comment