Blog
2019-09-01
This week, I've been in Cambridge for Talking Maths in Public (TMiP). TMiP is a conference for anyone involved in—or interested in getting involved
in—any sort of maths outreach, enrichment, or public engagement activity. It was really good, and I highly recommend coming to TMiP 2021.
The Saturday morning at TMiP was filled with a choice of activities, including a treasure punt (a treasure hunt on a punt) written by me. This post contains the puzzle from the treasure punt for
anyone who was there and would like to revisit it, or anyone who wasn't there and would like to give it a try. In case you're not current in Cambridge on a punt, the clues that you were meant to
spot during the punt are given behing spoiler tags (hover/click to reveal).
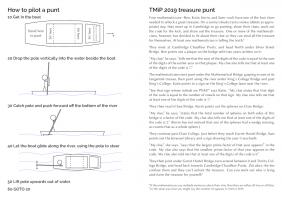
Instructions
Each boat was given a copy of the instructions, and a box that was locked using a combination lock.
If you want to make your own treasure punt or similar activity, you can find the LaTeX code used to create the instructions and the Python code I used to check that the puzzle
has a unique solution on GitHub. It's licensed with a CC BY 4.0
licence, so you can resuse an edit it in any way you like, as long as you attribute the bits I made that you keep.
The puzzle
Four mathematicians—Ben, Katie,
Kevin, and Sam—each have one of the four clues needed to unlock a great treasure.
On a sunny/cloudy/rainy/snowy (delete as appropriate) day, they meet up in Cambridge to go punting, share their clues, work out the code for the lock,
and share out the treasure. One or more of the mathematicians, however, has decided to lie about their clue so they can steal all the treasure for themselves.
At least one mathematician is telling the truth.
(If the mathematicians say multiple sentences about their clue, then they are either all true or all false.)
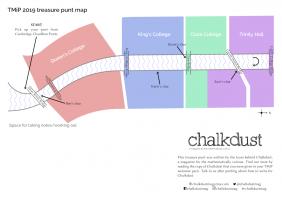
They meet at Cambridge Chauffeur Punts, and head North under Silver Street Bridge.
Ben points out a plaque on the bridge with two years written on it:
"My clue," he says, "tells me that the sum of the digits of the code is equal to the sum of the digits of the earlier year on that plaque (the year is 1702). My clue also tells me that at least one of the digits of the code is 7."
The mathematicians next punt under the Mathematical Bridge, gasping in awe at its tangential trusses, then punt along the river under King's College Bridge and past King's College.
Katie points to a sign on the King's College lawn near the river:
"See that sign whose initials are PNM?" says Katie. "My clue states that first digit of the code is equal to the number of vowels on that sign (The sign says "Private: No Mooring").
My clue also tells me that at least one of the digits of the code is 1."
They then reach Clare Bridge. Kevin points out the spheres on Clare Bridge:
"My clue," he says, "states that the total number of spheres on both sides of this bridge is a factor of the code (there are 14 spheres). My clue also tells me that at least one of the digits of the code is 2."
(Kevin has not noticed that one of the spheres had a wedge missing, so counts that as a whole sphere.)
They continue past Clare College. Just before they reach Garret Hostel Bridge, Sam points out the Jerwood Library and a sign showing the year it was built (it was built in 1998):
"My clue," she says, "says that the largest prime factor of that year appears in the code (in the same way that you might say the number 18 appears in 1018 or 2189).
My clue also says that the smallest prime factor of that year appears in the code. My clue also told me that at least one of the digits of the code is 0."
They then punt under Garret Hostel Bridge, turn around between it and Trinity College Bridge, and head back towards Cambridge Chauffeur Punts.
Zut alors, the lies confuse them and they can't unlock the treasure. Can you work out who is lying and claim the treasure for yourself?
The solution
The solution to the treasure punt is given below. Once you're ready to see it, click "Show solution".
(Click on one of these icons to react to this blog post)
You might also enjoy...
Comments
Comments in green were written by me. Comments in blue were not written by me.
Add a Comment
2019-07-03
This year's Big Internet Math-Off
is now underway with 15 completely new contestants (plus one returning contender). As I'm not the returning contestant, I haven't been spending
my time preparing my pitches. Instead, I've spent my time making an
unofficial Big Internet Math-Off sticker book.
To complete the sticker book, you will need to collect 162 different stickers. Every day, you will be given a pack of 5 stickers; there are
also some bonus packs available if you can find them (Hint: keep reading).
How many stickers will I need?
Using the same method as I did for last year's World Cup sticker book,
you can work out that the expected number of stickers needed to finish the sticker book:
If you have already stuck \(n\) stickers into your album, then the probability that the next sticker you get is new is
$$\frac{162-n}{162}.$$
The probability that the second sticker you get is the next new sticker is
$$\mathbb{P}(\text{next sticker is not new})\times\mathbb{P}(\text{sticker after next is new})$$
$$=\frac{n}{162}\times\frac{162-n}{162}.$$
Following the same method, we can see that the probability that the \(i\)th sticker you buy is the next new sticker is
$$\left(\frac{n}{162}\right)^{i-1}\times\frac{162-n}{162}.$$
Using this, we can calculate the expected number of stickers you will need to buy until you find a new one:
$$\sum_{i=1}^{\infty}i \left(\frac{162-n}{162}\right) \left(\frac{n}{162}\right)^{i-1} = \frac{162}{162-n}$$
Therefore, to get all 162 stickers, you should expect to buy
$$\sum_{n=0}^{161}\frac{162}{162-n} = 918 \text{ stickers}.$$
Using just your daily packs, it will take you until the end of the year to collect this many stickers.
Of course, you'll only need to collect this many if you don't swap your duplicate stickers.
How many stickers will I need if I swap?
To work out the expected number of stickers stickers you'd need if you swap, let's first think about two people who want to complete
their stickerbooks together. If there are \(a\) stickers that both collectors need and \(b\) stickers that one collector has and the other one
needs, then let \(E_{a,b}\) be the expected number of stickers they need to finish their sticker books.
The next sticker they get could be one of three things:
- A sticker they both need (with probability \(\frac{a}{162}\));
- A sticker one of them needs (with probability \(\frac{b}{162}\));
- A sticker they both have (with probability \(\frac{162-a-b}{162}\)).
Therefore, the expected number of stickers they need to complete their sticker books is
$$E_{a,b}=1+\frac{a}{162}E_{a-1,b+1}+\frac{b}{162}E_{a,b-1}+\frac{162-a-b}{162}E_{a,b}.$$
This can be rearranged to give
$$E_{a,b}=
\frac{162}{a+b}+
\frac{a}{a+b}E_{a-1,b+1}
+\frac{b}{a+b}E_{a,b-1}
$$
We know that $E_{0,0}=0$ (as if \(a=0\) and \(b=0\), both collectors have already finished their sticker books). Using this and the
formula above, we can work out that
$$E_{0,1}=162+E_{0,0}=162$$
$$E_{1,0}=162+E_{0,1}=324$$
$$E_{0,2}=\frac{162}2+E_{0,1}=243$$
$$E_{1,1}=\frac{162}2+\frac12E_{0,2}+\frac12E_{1,0}=364.5$$
... and so on until we find that \(E_{162,0}=1269\), and so our collectors should expect to collect 634 stickers each to complete their
sticker books.
For three people, we can work out that if there are \(a\) stickers that all three need, \(b\) stickers that two need, and \(c\) stickers
that one needs, then
$$
E_{a,b,c}
= \frac{162}{a+b+c}+
\frac{a}{a+b+c}E_{a-1,b+1,c}
+\frac{b}{a+b+c}E_{a,b-1,c+1}
+\frac{c}{a+b+c}E_{a,b,c-1}.
$$
In the same way as for two people, we find that \(E_{162,0,0}=1572\), and so our collectors should expect to collect 524 stickers each
to complete their sticker books.
Doing the same thing for four people gives an expected 463 stickers required each.
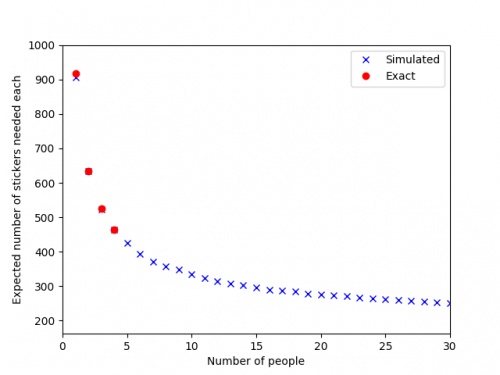
After four people, however, the Python code I wrote to do these calculations takes too long to run, so instead I approximated the numbers
by simulating 500 groups of \(n\) people collecting stickers, and taking the average number of stickers they needed. The results are shown in
the graph below.
The red dots are the expected values we calculated exactly, and the blue crosses are the simulated values.
It looks like you'll need to collect at least 250 stickers to finish the album: in order to get this many before the end of the Math-Off,
you'll need to find 20 bonus packs...
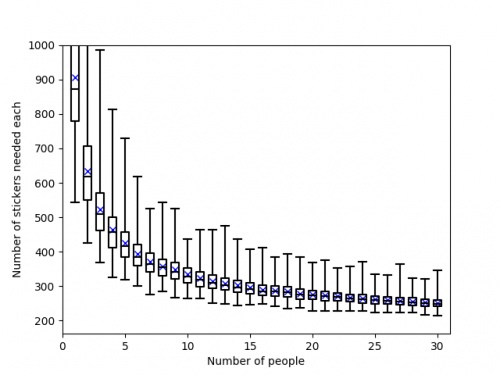
Of course, these are just the mean values and you could get lucky and need fewer stickers. The next graph shows box plots with the
quartiles of the data from the simulations.
So if you're lucky, you could complete the album with fewer stickers or fewer friends.
As a thank you for reading to the end of this blog post, here's a link that
will give you two bonus packs and help you on your way to the 250 expected stickers...
(Click on one of these icons to react to this blog post)
You might also enjoy...
Comments
Comments in green were written by me. Comments in blue were not written by me.
Link to sticker book, in the first paragraph, does not work. It points to mathoffstickbook.com
Pat Ashforth
minor typo for the 2 collector case
> and so our collectors should expect to collect 364 stickers
should be 634.
> and so our collectors should expect to collect 364 stickers
should be 634.
Road
Add a Comment
2019-06-19
A308092 The sum of the first \(n\) terms of the sequence is the concatenation of the first \(n\) bits of the sequence read as binary, with \(a(1) = 1\).1, 2, 3, 7, 14, 28, 56, 112, 224, 448, 896, 1791, 3583, 7166, ...

To understand this definition, let's look at the first few terms of this sequence written in binary:
By "the concatenation of the first \(n\) bits of the sequence", it means the first \(n\) binary digits of the whole sequence written in order:
1, then 11, then 110, then 1101, then 11011, then 110111, and so on. So the definition means:
- The first term is 1, as given in the definition (\(a(1)=1\)).
- The sum of the first 2 terms is the first 2 digits: \(1+10=11\).
- The sum of the first 3 terms is the first 3 digits: \(1+10+11=110\).
- The sum of the first 4 terms is the first 4 digits: \(1+10+11+111=1101\).
- The sum of the first 5 terms is the first 5 digits: \(1+10+11+111+1110=11011\).
As we know that the sum of the first \(n-1\) terms is the first \(n-1\) digits, we can calculate the third term of this sequence onwards using:
"\(a(n)\) is the concatenation of the first \(n\) bits of the sequence subtract concatenation of the first \(n-1\) bits of the sequence":
- The third term is \(110 - 11 = 11\).
- The fourth term is \(1101 - 110 = 111\).
- The fourth term is \(11011 - 1101 = 1110\).
- The fifth term is \(110111 - 11011 = 11100\).
The conjecture
Peter's conjecture is that the number of 1s in each term is greater than or equal to the number of 1s in the previous term.
I'm going to prove this conjecture. If you'd like to have a try first, stop reading now and come back when you're ready for spoilers.
(If you'd like a hint, read the next section then pause again.)
Adding a digit
The third term of the sequence onwards can be calculated by subtracting the first \(n-1\) digits from the first \(n\) digits.
If the first \(n-1\) digits form a binary number \(x\), then the first \(n\) digits will be \(2x+d\), where \(d\) is the \(n\)th digit
(because moving all the digits to the left one place in binary is multiplying by two).
Therefore the different is \(2x+d-x=x+d\), and so we can work out the \(n\)th term of the sequence by adding the \(n\)th digit in the
sequence to the first \(n-1\) digits. (Hat tip to Martin Harris, who spotted this first.)
Carrying
Adding 1 to a binary number the ends in 1 will cause 1 to carry over to the left. This carrying will continue until the 1 is carried into
a position containing 0, and after this all the digits to the left of this 0 will remain unchanged.
Therefore adding a digit to
the first \(n-1\) digits can only change the digits from the rightmost 0 onwards.
Endings
We can therefore disregard all the digits before the rightmost 0, and look at how the \(n\)th term compares to the \((n-1)\)th term.
There are 5 ways in which the first \(n\) digits could end:
- \(00\)
- \(010\)
- \(01...10\) (where \(1...1\) is a string of 2 or more ones)
- \(01\)
- \(01...1\) (where \(1...1\) is again a string of 2 or more ones)
We now look at each of these in turn and show that the \(n\)th term will contain at least as many ones at the \((n-1)\)th term.
Case 1: \(00\)
If the first \(n\) digits of the sequence are \(x00\) (a binary number \(x\) followed by two zeros), then the \((n-1)\)th term of the
sequence is \(x+0=x\), and the \(n\)th term of the sequence is \(x0+0=x0\). Both \(x\) and \(x0\) contain the same number of ones.
Case 2: \(010\)
If the first \(n\) digits of the sequence are \(x010\), then the \((n-1)\)th term of the sequence is \(x0+1=x1\),
and the \(n\)th term of the sequence is \(x01+0=x01\). Both \(x1\) and \(x01\) contain the same number of ones.
Case 3: \(01...10\)
If the first \(n\) digits of the sequence are \(x01...10\), then the \((n-1)\)th term of the sequence is \(x01...1+1=x10...0\),
and the \(n\)th term of the sequence is \(x01...10+1=x01...1\). \(x01...1\) contains more ones than \(x10...0\).
Case 4: \(01\)
If the first \(n\) digits of the sequence are \(x01\), then the \((n-1)\)th term of the sequence is \(x+0=x\),
and the \(n\)th term of the sequence is \(x0+1=x1\). \(x1\) contains one more one than \(x\).
Case 5: \(01...1\)
If the first \(n\) digits of the sequence are \(x01...1\), then the \((n-1)\)th term of the sequence is \(x01...1+1=x10...0\),
and the \(n\)th term of the sequence is \(x01...1+1=x10...0\). Both these contain the same number of ones.
In all five cases, the \(n\)th term contains more ones or an equal number of ones to the \((n-1)\)th term, and so the conjecture is true.
(Click on one of these icons to react to this blog post)
You might also enjoy...
Comments
Comments in green were written by me. Comments in blue were not written by me.
Add a Comment
2019-04-09
In the latest issue of Chalkdust,
I wrote an article
with Edmund Harriss about the Harriss spiral that appears on the cover of the magazine.
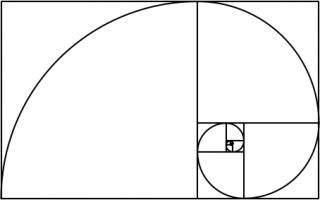
To draw a Harriss spiral, start with a rectangle whose side lengths are in the plastic ratio; that is the ratio \(1:\rho\)
where \(\rho\) is the real solution of the equation \(x^3=x+1\), approximately 1.3247179.
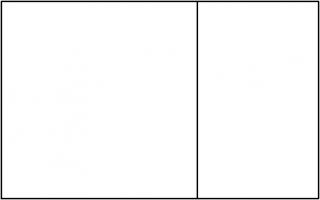
This rectangle can be split into a square and two rectangles similar to the original rectangle. These smaller rectangles can then be split up in the same manner.
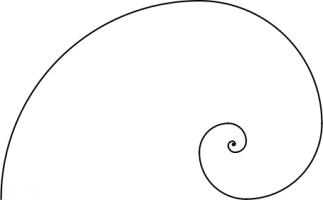
Drawing two curves in each square gives the Harriss spiral.
This spiral was inspired by the golden spiral, which is drawn in a rectangle whose side lengths are in the golden ratio of \(1:\phi\),
where \(\phi\) is the positive solution of the equation \(x^2=x+1\) (approximately 1.6180339). This rectangle can be split into a square and one
similar rectangle. Drawing one arc in each square gives a golden spiral.
The golden and Harriss spirals are both drawn in rectangles that can be split into a square and one or two similar rectangles.
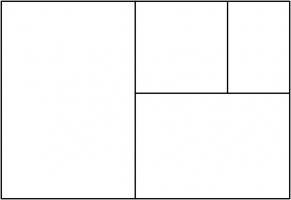
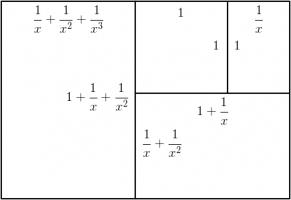
Continuing the pattern of these arrangements suggests the following rectangle, split into a square and three similar rectangles:
Let the side of the square be 1 unit, and let each rectangle have sides in the ratio \(1:x\). We can then calculate that the lengths of
the sides of each rectangle are as shown in the following diagram.
The side lengths of the large rectangle are \(\frac{1}{x^3}+\frac{1}{x^2}+\frac2x+1\) and \(\frac1{x^2}+\frac1x+1\). We want these to also
be in the ratio \(1:x\). Therefore the following equation must hold:
$$\frac{1}{x^3}+\frac{1}{x^2}+\frac2x+1=x\left(\frac1{x^2}+\frac1x+1\right)$$
Rearranging this gives:
$$x^4-x^2-x-1=0$$
$$(x+1)(x^3-x^2-1)=0$$
This has one positive real solution:
$$x=\frac13\left(
1
+\sqrt[3]{\tfrac12(29-3\sqrt{93})}
+\sqrt[3]{\tfrac12(29+3\sqrt{93})}
\right).$$
This is equal to 1.4655712... Drawing three arcs in each square allows us to make a spiral from a rectangle with sides in this ratio:
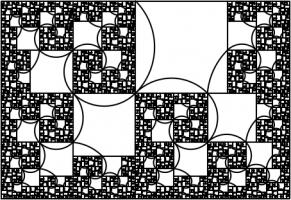
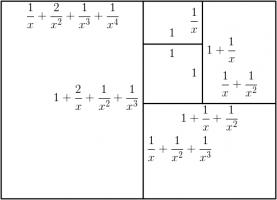
Adding a fourth rectangle leads to the following rectangle.
The side lengths of the largest rectangle are \(1+\frac2x+\frac3{x^2}+\frac1{x^3}+\frac1{x^4}\) and \(1+\frac2x+\frac1{x^2}+\frac1{x^3}\).
Looking for the largest rectangle to also be in the ratio \(1:x\) leads to the equation:
$$1+\frac2x+\frac3{x^2}+\frac1{x^3}+\frac1{x^4} = x\left(1+\frac2x+\frac1{x^2}+\frac1{x^3}\right)$$
$$x^5+x^4-x^3-2x^2-x-1 = 0$$
This has one real solution, 1.3910491... Although for this rectangle, it's not obvious which arcs to draw to make a
spiral (or maybe not possible to do it at all). But at least you get a pretty fractal:
We could, of course, continue the pattern by repeatedly adding more rectangles. If we do this, we get the following polynomials
and solutions:
| Number of rectangles | Polynomial | Solution |
| 1 | \(x^2 - x - 1=0\) | 1.618033988749895 |
| 2 | \(x^3 - x - 1=0\) | 1.324717957244746 |
| 3 | \(x^4 - x^2 - x - 1=0\) | 1.465571231876768 |
| 4 | \(x^5 + x^4 - x^3 - 2x^2 - x - 1=0\) | 1.391049107172349 |
| 5 | \(x^6 + x^5 - 2x^3 - 3x^2 - x - 1=0\) | 1.426608021669601 |
| 6 | \(x^7 + 2x^6 - 2x^4 - 3x^3 - 4x^2 - x - 1=0\) | 1.4082770325090774 |
| 7 | \(x^8 + 2x^7 + 2x^6 - 2x^5 - 5x^4 - 4x^3 - 5x^2 - x - 1=0\) | 1.4172584399350432 |
| 8 | \(x^9 + 3x^8 + 2x^7 - 5x^5 - 9x^4 - 5x^3 - 6x^2 - x - 1=0\) | 1.412713760332943 |
| 9 | \(x^{10} + 3x^9 + 5x^8 - 5x^6 - 9x^5 - 14x^4 - 6x^3 - 7x^2 - x - 1=0\) | 1.414969877544769 |
The numbers in this table appear to be heading towards around 1.414, or \(\sqrt2\).
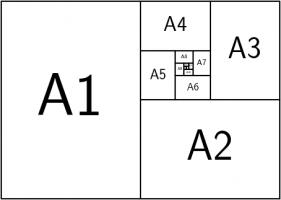
This shouldn't come as too much of a surprise because \(1:\sqrt2\) is the ratio of the sides of A\(n\) paper (for \(n=0,1,2,...\)).
A0 paper can be split up like this:
This is a way of splitting up a \(1:\sqrt{2}\) rectangle into an infinite number of similar rectangles, arranged following the pattern,
so it makes sense that the ratios converge to this.
Other patterns
In this post, we've only looked at splitting up rectangles into squares and similar rectangles following a particular pattern. Thinking about
other arrangements leads to the following question:
Given two real numbers \(a\) and \(b\), when is it possible to split an \(a:b\) rectangle into squares and \(a:b\) rectangles?
If I get anywhere with this question, I'll post it here. Feel free to post your ideas in the comments below.
(Click on one of these icons to react to this blog post)
You might also enjoy...
Comments
Comments in green were written by me. Comments in blue were not written by me.
@g0mrb: CORRECTION: There seems to be no way to correct the glaring error in that comment. A senior moment enabled me to reverse the nomenclature for paper sizes. Please read the suffixes as (n+1), (n+2), etc.
(anonymous)
I shall remain happy in the knowledge that you have shown graphically how an A(n) sheet, which is 2 x A(n-1) rectangles, is also equal to the infinite series : A(n-1) + A(n-2) + A(n-3) + A(n-4) + ... Thank-you, and best wishes for your search for the answer to your question.
g0mrb
Add a Comment
2019-03-26
I originally wrote this post for The Aperiodical.
A few months ago, Adam Townsend went to lunch and had a conversation. I wasn't there, but I imagine the conversation went something like this:
Adam: Hello.Smitha: Hello.Adam: How are you?Smitha: Not bad. I've had a funny idea, actually.Adam: Yes?Smitha: You know how the \hat command in LaTeΧ puts a caret above a letter?... Well I was thinking it would be funny if someone made a package that made the \hat command put a picture of an actual hat on the symbol instead?Adam: (After a few hours of laughter.) I'll see what my flatmate is up to this weekend...Jeff: What on Earth are you two talking about?!

As anyone who has been anywhere near maths at a university in the last ∞ years will be able to tell you,
LaTeΧ is a piece of maths typesetting software. It's a bit like a version of Word that runs in terminal and makes PDFs with really
pretty equations.
By default, LaTeΧ can't do very much, but features can easily added by importing packages: importing the graphicsx
package allows you to put images in your PDF; importing geometry allows you to easily change the page margins; and importing
realhats makes the \hat command put real hats above symbols.
Changing the behaviour of \hat
By default, the LaTeΧ command \hat puts a pointy "hat" above a symbol:
After Adam's conversation, we had a go at redefining the \hat command by putting the following
at the top of our LaTeΧ file.
LaTeΧ
\renewcommand{\hat}[1]{% We put our new definition here
}
After a fair amount of fiddling with the code, we eventually got it to produce the following result:
We were now ready to put our code into a package so others could use it.
How to write a package
A LaTeΧ package is made up of:
- a sty file, containing a collection of commands like the one we wrote above;
- a PDF of documentation showing users how to use your package;
- a README file with a basic description of your package.
It's quite common to make the first two of these by making a
dtx file
and an ins file. And no, we have
no idea either why these are the file extensions used or why this is supposedly simpler than making a sty file and a PDF.
The ins file says which bits of the dtx should be used to make up the sty file.
Our ins file looks like this:
LaTeΧ
\input{docstrip.tex}\keepsilent
\usedir{tex/latex/realhats}
\preamble
*License goes here*
\endpreamble
\askforoverwritefalse
\generate{
\file{realhats.sty}{\from{realhats.dtx}{realhats}}
}
\endbatchfile
The most important command in this file is \generate: this says that that the file
realhats.sty should be made from the file realhats.dtx
taking all the lines that are marked as part of realhats. The following is part of our dtx file:
LaTeΧ
%\lstinline{realhats} is a package for \LaTeX{} that makes the \lstinline{\hat}%command put real hats on symbols.
%For example, the input \lstinline@\hat{a}=\hat{b}@ will produce the output:
%\[\hat{a}=\hat{b}\]
%To make a vector with a hat, the input \lstinline@\hat{\mathbf{a}}@ produces:
%\[\hat{\mathbf{a}}\]
%
%\iffalse
%<*documentation>
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{realhats}
\usepackage{doc}
\usepackage{listings}
\title{realhats}
\author{Matthew W.~Scroggs \& Adam K.~Townsend}
\begin{document}
\maketitle
\DocInput{realhats.dtx}
\end{document}
%</documentation>
%\fi
%\iffalse
%<*realhats>
\NeedsTeXFormat{LaTeX2e}
\ProvidesPackage{realhats}[2019/02/02 realhats]
\RequirePackage{amsmath}
\RequirePackage{graphicx}
\RequirePackage{ifthen}
\renewcommand{\hat}[1]{
% We put our new definition here
}
%</realhats>
%\fi
The lines near the end between <*realhats>
and </realhats> will be included in the sty file, as they are marked at part of
realhats.
The rest of this file will make the PDF documentation when the dtx file is compiled.
The command \DocInput tells LaTeΧ to include the dtx again, but with the
%s that make lines into comments removed. In this way all the comments that describe the functionality will end up
in the PDF. The lines that define the package will not be included in the PDF as they are between \iffalse and
\fi.
Writing both the commands and the documentation in the same file like this means that the resulting file is quite a mess, and really quite
ugly. But this is apparently the standard way of writing LaTeΧ packages, so rest assured that it's not just our code that ugly and
confusing.
What to do with your package
Once you've written a package, you'll want to get it out there for other people to use. After all, what's the point of being able to
put real hats on top of symbols if the whole world can't do the same?
First, we put the source code of our package on GitHub, so that Adam and I had an
easy way to both work on the same code. This also allows other LaTeΧ lovers to see the source and contribute to it, although none have
chosen to add anything yet.
Next, we submitted our package to CTAN, the Comprehensive TeΧ Archive Network.
CTAN is an archive of thousands of LaTeΧ packages, and putting realhats there gives LaTeΧ users
everywhere easy access to real hats. Within days of being added to CTAN, realhats was added (with no work by us)
to MikTeX and TeX Live
to allow anyone using these LaTeΧ distributions to seemlessly install it as soon as it is needed.
We figured that the packaged needed a website too, so we made one. We also figured that the website
should look as horrid as possible.
How to use realhats
So if you want to end fake hats and put real hats on top of your symbols, you can simply write \usepackage{realhats}
at the top of your LaTeΧ file.

realhats: gotta put them all in academic papers
(Click on one of these icons to react to this blog post)
You might also enjoy...
Comments
Comments in green were written by me. Comments in blue were not written by me.
I am a pensioner studying maths with OU. Currently doing M248 stats module. My enjoyment of MLEs has been magnified by your wonderful realhats package. It's a good job I'm 99% tee-total or my tutor would be getting a dubious assignment (still leaves a 1% chance of malt-driven mischief though).
Dave
Add a Comment