Blog
A 20,000-to-1 baby?
2018-03-23
This morning, I heard about Arnie Ellis on the Today programme. Arnie is the first baby boy to be born in his family in five generations, following ten girls. According to John Humphrys, there is a 20,000-to-1 chance of this happening. Pretty quickly, I started wondering where this number came from.
After a quick Google, I found that this news story had appeared in many of today's papers, including the Sun and the Daily Mail. They all featured this 20,000-to-1 figure, which according to The Sun originally came from Ladbrokes.
What is the chance of this happening?
If someone is having a child, the probability of it being a girl is 0.5. The probability of it being a boy is also 0.5. So the probaility of having ten girls followed by a boy is
$$\left(\tfrac12\right)^{10}\times\tfrac12=\frac1{2048}.$$
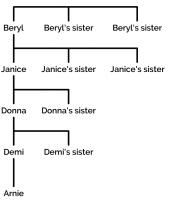
If all 11 children were siblings, then this would be the chance of this happening—and it's a long way off the 20,000-to-1. But in Arnie's case, the situation is different. Luckily in the Daily Mail article, there is an outline of Arnie's family tree.
Here, you can see that the ten girls are spread over five generations. So the question becomes: given a baby, what is the probability that the child is male and his most recently born ten relatives on their mother's side are all female?
Four of the ten relatives are certainly female—Arnie's mother, grandmother, great grandmother and great great grandmother are all definitely female. This only leaves six more relatives, so the probability of a baby being in Arnie's position is
$$\left(\tfrac12\right)^{6}\times\tfrac12=\frac1{128}.$$
This is now an awful lot lower than the 20,000-to-1 we were told. In fact, with around 700,000 births in the UK each year, we'd expect over 5,000 babies to be born in this situation every year. Maybe Arnie's not so rare after all.
This number is based on the assumption that the baby's last ten relatives are spread across five generations. But the probability will be different if the relatives are spread over a different number of generations. Calculating the probability for a baby with any arrangement of ancestors would require knowing the likelihood of each arrangement of relatives, which would require a lot of data that probably doesn't exist. But the actual anwer is probably not too far from 127-to-1.
Where did 20,000-to-1 come from?
This morning, I emailed Ladbrokes to see if they could shed any light on the 20,000-to-1 figure. They haven't got back to me yet. (Although they did accidentally CC me when sending the query on to someone who might know the answer, so I'm hopeful.) I'll update this post with an explanaation if I do hear back.
Until then, there is one possible explanation for the figure: we have looked at the probability that a baby will be in this situation, but we could instead have started at the top of the family tree and looked at the probability that Beryl's next ten decendents were girls followed by a boy. The probability of this happening will be lower, as there is a reasonable chance that Beryl could have no female children, or no children at all. Looking at the problem this way, there are more ways for the situation to not happen, so the probability of it happening is lower.
But working the actually probability out in this way would again require data about how many children are likely in each generation, and would be a complicated calculation. It seems unlikely that this is what Ladbrokes did. Let's hope they shed some light on it...
(Click on one of these icons to react to this blog post)
You might also enjoy...
Comments
Comments in green were written by me. Comments in blue were not written by me.
2018-12-10
@Steve Spivey: NothingMatthew
Add a Comment