Blog
Building MENACEs for other games
2018-04-29
Two years ago, I built a copy of MENACE (Machine Educable Noughts And Crosses Engine). Since then, it's been to many Royal Institution masterclasses, visted Manchester and met David Attenborough. When I'm not showing them off, the 304 matchboxes that make up my copy of MENACE live in this box:
This box isn't very big, which might lead you to wonder how big MENACE-style machines would be for other games.
Hexapawn (HER)
In A matchbox game learning-machine by Martin Gardner [1], the game of Hexapawn was introduced. Hexapawn is played on a 3×3 grid, and starts with three pawns facing three pawns.
The pieces move like pawns: they may be either moved one square forwards into an empty square, or take another pawn diagonally (the pawns are not allowed to move forwards two spaces on their first move, as they can in chess).
You win if one of your pawns reaches the other end of the board. You lose if none of your pieces can move.
The game was invented by Martin Gardner as a good game for his readers to build a MENACE-like machine to play against, as there are only 19 positions that can face player two, so only 19 matchboxes are needed to make HER (Hexapawn Educable Robot). (HER plays as player two, as if player two plays well they can always win.)
Nine Men's Morris (MEME)
In Nine Men's Morris, two players first take turns to place pieces on the board, before taking turns to move pieces to adjacent spaces. If three pieces are placed in a row, a player may remove one of the opponent's pieces. It's a bit like Noughts and Crosses, but with a bit more chance of it not ending in a draw.
In Solving Nine Men's Morris by Ralph Gasser [2], the number of possible game states in Nine Men's Morris is given as approximately \(10^{10}\). To build MEME (Machine Educable Morris Engine), you would need this many matchboxes. These boxes would form a sphere with radius 41m: that's approximately the length of two tennis courts.
As a nice bonus, if you build MEME, you'll also smash the world record for the largest matchbox collection.
Connect 4 (COFFIN)
In Symbolic classification of general two-player games by Stefan Edelkamp and Peter Kissmann [3], the number of possible game states in Connect 4 is given as 4,531,985,219,092. The boxes used to make COFFIN (COnnect Four Fighting INstrument) would make a sphere with radius 302m: approximately the height of the Eiffel Tower.
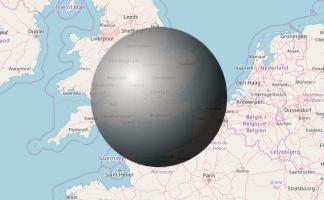
In Solving the game of Checkers by Jonathan Schaeffer and Robert Lake [4], the number of possible game states in Draughts is given as approximately \(5\times10^{20}\). The boxes needed to build DOCILE (Draughts Or Checkers Intelligent Learning Engine) would make a sphere with radius 151km.
DOCILE: Draughts Or Checkers Intelligent Learning Engine
If the centre of DOCILE was in London, some of the boxes would be in Sheffield.
Chess (CLAWS)
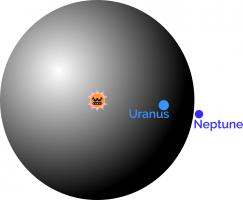
The number of possible board positions in chess is estimated to be around \(10^{43}\). The matchboxes needed to make up CLAWS (Chess Learning And Winning System) would fill a sphere with radius \(4\times10^{12}\)m.
If the Sun was at the centre of CLAWS, you might have to travel past Uranus on your search for the right box.
Go (MEGA)
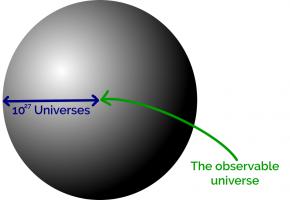
The number of possible positions in Go is estimated to be somewhere near \(10^{170}\). To build MEGA (Machine Educable Go Appliance), you're going to need enough matchboxes to make a sphere with radius \(8\times10^{54}\)m.
The observable universe takes up a tiny space at the centre of this sphere. In fact you could fit around \(10^{27}\) copies of the universe side by side along the radius of this sphere.
It's going to take you a long time to look through all those matchboxes to find the right one...
References
[3] Symbolic classification of general two-player games by Stefan Edelkamp and Peter Kissmann. in Advances in Artificial Intelligence (edited by A.R. Dengel, K. Berns, T.M. Breuel, F. Bomarius, T.R. Roth-Berghofer), 2008. [link]
[4] Solving the game of Checkers by Jonathan Schaeffer and Robert Lake. Games of No Chance 29, 1996. [link]
(Click on one of these icons to react to this blog post)
You might also enjoy...
Comments
Comments in green were written by me. Comments in blue were not written by me.
2022-07-31
Kind of like the "Blue Brain Project". They got a worm and fruitfly brain on the computer, I wanted to download the fruitfly brain for 2GB USB stick but it was over 12 TB. They uploaded half a mouse brain on their project so far. Willem
Would Love to play with Coffin/Coffin2. Do you have the code on git or a JS/web version?... been kind of thinking of coding a version that only makes the match boxes as it needs them (to save on memory) but I heard you already have a version with optimizations (and my coding skill is rough at best)
John
Are you aware of any actual implementations of anything in matchboxes, games or otherwise?
Jam
Of course, to make CLAWS, you will have to leave a large gap in the centre of the matchbox sphere, to avoid the very real danger of fire. Furthermore, some redundancy is needed, to replace the boxes which will be damaged by the myriad hard objects which are whizzing around the solar system. For this latter reason alone, I propose that the machine would be impractical to make! ;-D
g0mrb
Add a Comment